Bloom's Taxonomy
Revised for 21st-Century Learners
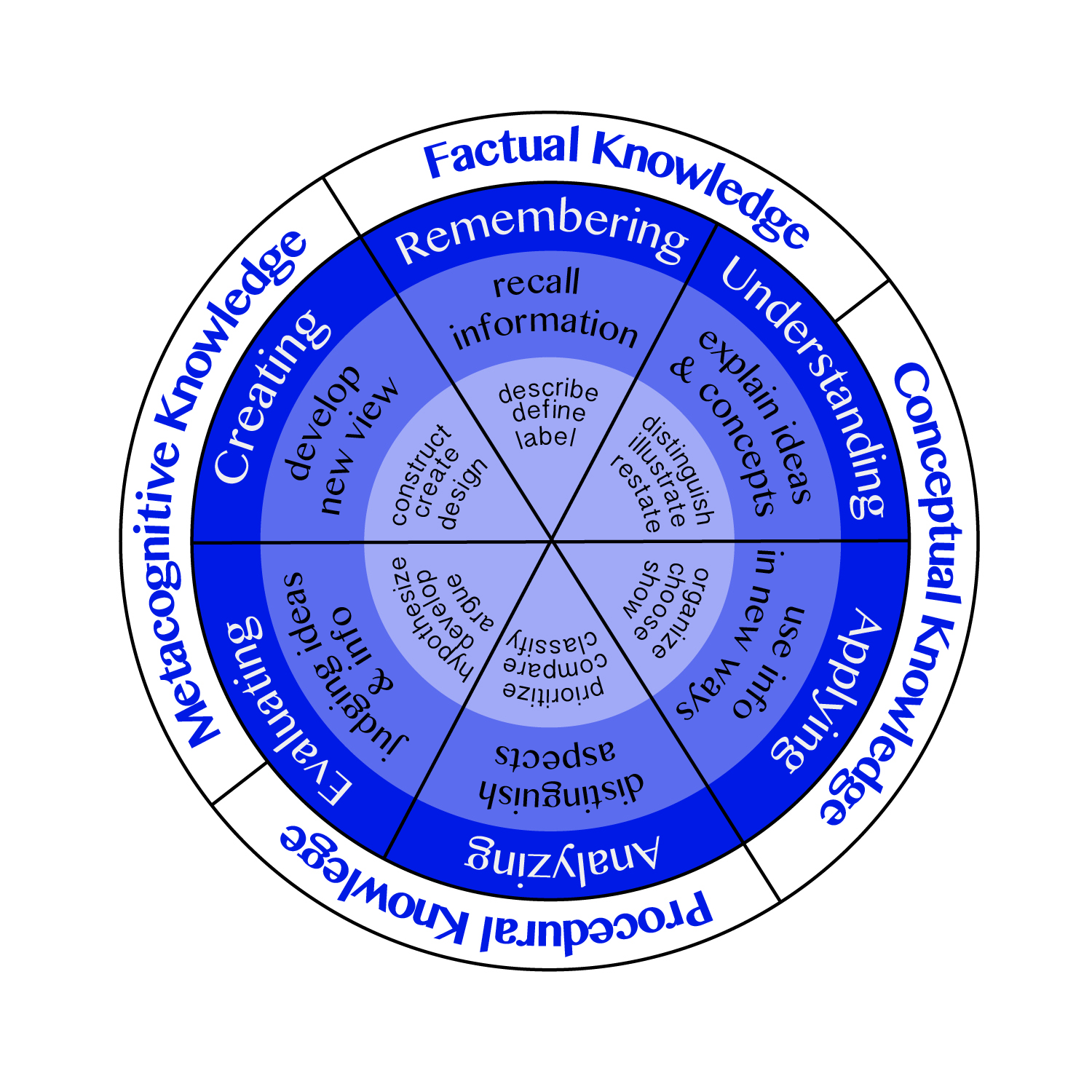
Benjamin Bloom led a team of researchers in the 1950s to establish behaviors associated with learning; the outcome of this study was Bloom’s Taxonomy of Learning (1956). Forty years later, one of his students, Lorin Anderson, revised the taxonomy to accommodate progressions in pedagogy. The revised taxonomy has altered categories and now includes verbs associated with each of the six aspects of cognition.
The graph demonstrates the six aspects of learning, Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating, in combination with a brief explanation of the process, and verbs teachers can use to get students to think on these levels. Here, Bloom’s Taxonomy is situated in the four types of knowledge, Factual Knowledge of terminology and details, Conceptual Knowledge of relationships among pieces of concepts or theories, Procedural Knowledge of processes and methods of theories and problems, and Metacognitive Knowledge of learning strategies and processes. This chart starts with factual knowledge and remembering and builds in complexity as it moves clockwise. A comprehensive lesson will require students to apply multiple types of knowledge and cognitive skills.
| Level | Verbs & Sample Objectives | Discussion Questions |
|---|---|---|
|
Remember Be able to recall information such as dates, events, places, ideas, definitions, formulas, and theories. |
Arrange, Define, Describe, Detail, Draw, Duplicate, Identify, Indicate, Inventory, Label, List, Locate, Match, Name, Outline, Pick, Point, Pronounce, Quote, Recall, Recite, Recognize, Record, Relate, Repeat, Reproduce, Restate, State, Underline
|
|
|
Understand Be able to grasp the meaning of the information, express it in own words, and/or cite examples. |
Classify, Confirm, Contrast, Convert, Decipher, Defend, Designate, Differentiate, Equate, Estimate, Examine, Express, Extend, Extrapolate, Generalize, Give Examples, Group, Infer, Interpret, Order, Paraphrase, Predict, Rephrase, Rewrite, Sort, Specify, Substitute, Tell, Translate
|
|
|
Apply Be able to apply knowledge or skills to new situations. Use information and knowledge to solve a problem, answer a question, or perform another task. |
Add, Allocate, Alter, Apply, Calculate, Change, Choose, Complete, Compute, Conduct, Coordinate, Demonstrate, Determine, Direct, Discover, Divide, Dramatize, Draw, Employ, Formulate, Gather, Graph, Make, Manipulate, Model, Multiply, Operate, Perform, Present, Provide, Recount, Report, Schedule, Show, Sketch, Subtract, Use, Utilize
|
|
|
Analyze Be able to break down knowledge into parts and show and explain the relationships among the parts. |
Analyze, Appraise, Associate, Break Down, Criticize, Discern, Diagram, Discriminate, Dissect, Distinguish, Elect, Establish, Explain, Expound, Illustrate, Inspect, Profile, Question, Refute, Separate, Simplify, Subdivide, Summarize, Test
|
|
|
Evaluate Be able to judge or assess the value of material and methods for a given purpose. |
Argue, Assess, Attack, Compare and Contrast, Conclude, Critique, Debate, Decide, Deduce, Diagnose, Evaluate, Forecast, Improve, Judge, Justify, Measure, Prioritize, Prove, Rank, Rate, Recommend, Resolve, Revise, Select, Solve, Support, Value, Verify, Weigh
|
|
|
Create Be able to pull together parts of knowledge to form a new whole and build relationships for new situations. |
Assemble, Assimilate, Categorize, Collect, Combine, Compile, Compose, Condense, Construct, Create, Design, Derive, Develop, Devise, Elaborate, Expand, Generate, Guide, Hypothesize, Integrate, Invent, Manage, Modify, Organize, Plan, Prepare, Prescribe, Produce, Propose, Rearrange, Reconstruct, Reorganize, Rework, Set Up, Synthesize, Theorize, Transform, Write
|
|
References:
Table adapted from: Anderson, L.W., & Krathwohl, D.R. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing, abridged edition. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Wheel adapted from: Edutechalogy. Retrieved from http://eductechalogy.org/swfapp/blooms/wheel/engage.swf
 View and download Bloom's Taxonomy PDF
View and download Bloom's Taxonomy PDF
